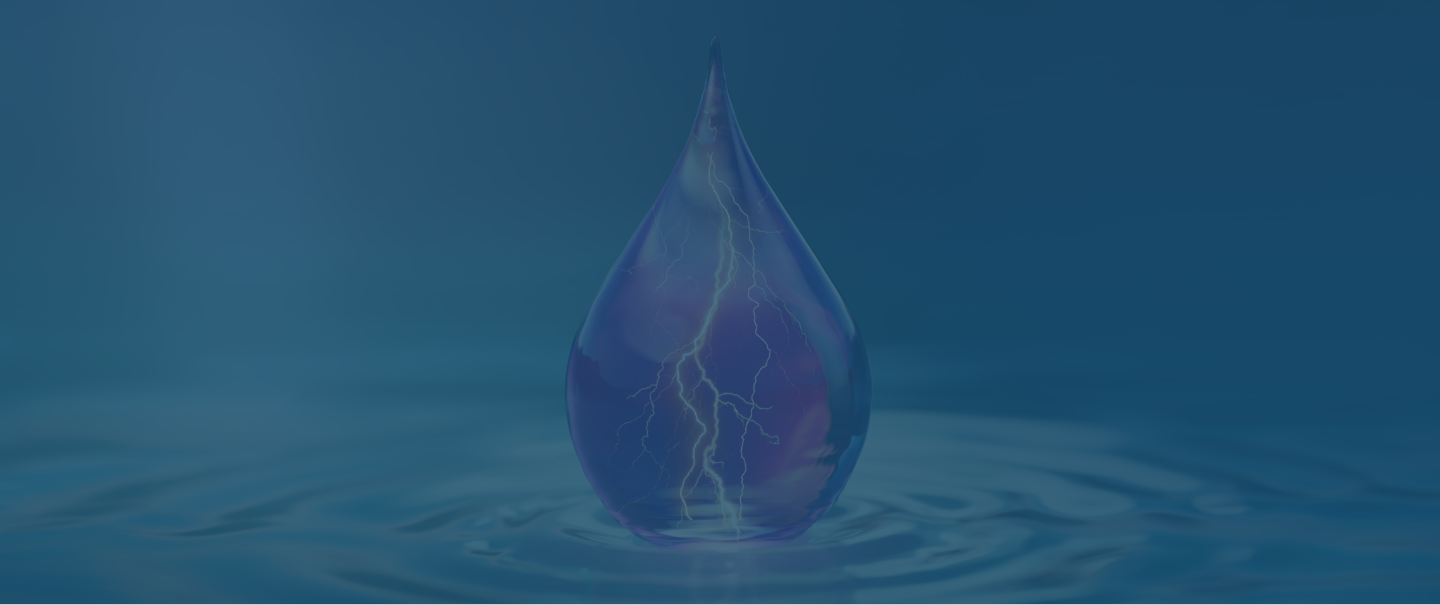
TRANSFORMATION BEGINS INSIDE
PRODRUG ACTIVATION
Strong, effective corneal penetration1,2
SEE IT IN ACTION
Watch the mechanism of action for ILEVRO®
AFTER TOPICAL OCULAR DOSING
ILEVRO® enters the cornea as nepafenac, delivering an analgesic effect to the corneal surface.2,3
Nepafenac, a neutral molecule, may have stronger corneal penetration than other NSAIDs.4
Nepafenac quickly crosses the cornea and is converted by ocular tissue hydrolases within the anterior chamber to a more potent NSAID, amfenac, with peak concentrations in <1 hour.1,2,4,5
Nepafenac and amfenac are thought to inhibit the action of prostaglandin H synthase (cyclooxygenase), an enzyme required for prostaglandin production.3
Effective inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2
Nepafenac and amfenac, both NSAIDs, are thought to inhibit the action of cyclooxygenase (COX),
an enzyme required for prostaglandin production.1
Amfenac is a potent inhibitor of both COX-1 and COX-2 isoforms.3
Smaller particle size, twice the drug concentration6,7
Compared with Nevanac®, ILEVRO® offers:
Enhanced viscosity and an added retention agent to improve bioavailability7,8
Approximately 40% smaller particle size7
Increased surface area of dissolution8
Twice the drug concentration delivered in target tissue6
These characteristics are not intended to imply superior safety or efficacy.
Ready for once-daily postoperative use
Your patients may be able to save on their script
Data provided through MMIT and are current as of 2/2024. The information provided in this website is not a guarantee of coverage or payment (partial or full). Actual benefits are determined by each plan administrator in accordance with its respective policy and procedures. Nothing herein may be construed as an endorsement, approval, recommendation, representation or warranty of any kind by any plan or insurer referenced herein.
References: 1. ILEVRO (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.3% [package insert]. Harrow IP, LLC; 2023. 2. Ke TL, Graff G, Spellman JM, Yanni JM. Nepafenac, a unique nonsteroidal prodrug with potential utility in the treatment of trauma-induced ocular inflammation: II. In vitro bioactivation and permeation of external ocular barriers. Inflammation. 2000;24(4):371-384. 3. Gamache DA, Graff G, Brady MT, Spellman JM, Yanni JM. Nepafenac, a unique nonsteroidal prodrug with potential utility in the treatment of trauma-induced ocular inflammation: I. Assessment of anti-inflammatory efficacy. Inflammation. 2000;24(4):357-370. 4. Lindstrom R, Kim T. Ocular permeation and inhibition of retinal inflammation: an examination of data and expert opinion on the clinical utility of nepafenac. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22(2):397-404. 5. Walters T, Raizman M, Ernest P, Gayton J, Lehmann R. In vivo pharmacokinetics and in vitro pharmacodynamics of nepafenac, amfenac, ketorolac, and bromfenac. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:1539-1545. 6. Data on file. Harrow IP, LLC; 2023. 7. Goldman DA. Ilevro––This Isn’t Your Father’s NSAID. Ophthalmology Web. Accessed September 13, 2023. www.ophthalmologyweb.com/Featured-Articles/136201-Ilevro-This-Isn-t-Your-Father-s-NSAID 8. Modi SS, Lehmann RP, Walters TR, et al. Once-daily nepafenac ophthalmic suspension 0.3% to prevent and treat ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery: phase 3 study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(2):203-211.